

|
20V Motronic ECU System 1991 200TQ and 1992-95 S4/S6 with 20V Turbo Engine Oxygen (O2) Sensor, Open Loop and Closed Loop Operation The oxygen sensor is mounted in the exhaust pipe just after the turbo exit. The O2 sensor has a internal heating element to ensure quick warm up and correct operation at idle. There are three wires going into the O2 sensor on the Audi Turbos. One ground, one +12V signal, and one for the actual O2 sensor output voltage. On the 20V 3B engines, the +12V for the heating element is provided by the fuel pump relay through fuse #29 (10A) so this circuit should be checked if you have problems with the O2 sensor working at idle. The 1992-95 S4/S6 use a 12A circuit breaker or fuse (S73) located in the Aux Relay Panel III under the passenger side lower right kick panel to supply the O2 sensor heater circuit. (USA Left hand drive) The O2 sensor incorporates a vent to outside ambient air for a reference to compare to the oxygen level in the exhaust gas. This vent is normally in the area where the wires exit the sensor, so be careful not to get water or other debris in the top of the O2 sensor when cleaning the engine. A slow responding O2 sensor that has been contaminated, or is just out and tired out, can cause some surging while cruising at steady speed, poor acceleration or hesitation. If you suspect you have a slow responding or defective O2 sensor, you can temporarily disconnect the single black lead from the O2 sensor and then drive the vehicle again to see if the poor running was caused by a defective sensor. You may want to also clear the ECU adaptation memory during this test. ECU Memory Information After replacing the O2 sensor, or after reconnecting the single black wire, you should also clear any stored fault codes. ECU Fault Code Information. Bosch recommends replacing the O2 sensor every 60k miles to ensure low emissions and efficient engine operation to get the highest gas mileage possible. I can supply the OEM replacement sensor with the correct wiring harness, or the lower cost 3 wire Universal Heated O2 sensor. Audi parts on-line catalog Here is a picture of the O2 sensor with it removed from the exhaust down pipe. 
 O2 Sensor Location in the 1992-95 Audi S4/S6 When the engine is first started when it is cold, the engine will briefly run for 1 or 2 minutes in open loop operation based on the "basic" idle mixture setting in the Mass Air Flow Meter (MAF) and by the control information programmed into the Motronic ECU. Normally the basic idle mixture is set to be 0.6% to 1.2% Carbon Monoxide (CO) when the exhaust gas is measured up stream of the catalytic converter. Once the Oxygen (O2) Sensor warms up (Heated O2 sensor), the system will switch over to closed loop operation. This sensor is used to monitor oxygen levels in the exhaust and acts as a voltage supply that transitions high to low when the oxygen level is high (slightly lean above 14:7 to 1 air fuel ratio) and transitions low to high when the Oxygen level is low (slightly rich air fuel mixture below 14:7 to 1 air fuel ratio). The ECU uses this oxygen sensor signal to tweak the air fuel mixture back and forth close to the ideal 14.7 to 1 Air Fuel Ratio. With the fuel system in closed loop operation after the O2 sensor warms up, the O2 sensor voltage cycles up and down between ~0.1V and ~0.9V. At idle, the O2 voltage should cycle back and forth 1 to 2 times per second and when cruising, it should cycle back and forth ~4 to 5 times per second. This cycling occurs because the engine computer senses the O2 voltage and then changes the pulse width of the signal driving the fuel injector on and off. This switching action allows the ECU to do minor adjustments to the air fuel ratio to allow the catalytic converter to perform its job to optimize the "oxidation" of Carbon Monoxide (CO) and Hydrocarbons (HC) and the reduction of Nitrogen Oxides (NOx). The oxidation occurs when the mixture is slightly lean and more oxygen is available, and the reduction occurs when the mixture is slightly rich and less oxygen is available. These chemical reactions that occur in the catalytic converter ensure the lowest possible emissions out the tailpipe. Catalytic converters typically operate at 60-90% efficiency depending on age. This means that the amount of exhaust emissions that enter the catalytic converter are reduced approximately by this percentage. For example, in the Audi I5 turbo engine, at idle, you typically have exhaust gas entering the catalytic converter with a Carbon Monoxide (CO) level of 1.2%, this will be reduced to 0.36% to as measured at the tailpipe with a 70% efficient converter. Here is a chart showing the relationship between the various exhaust gases and air/fuel ratios. 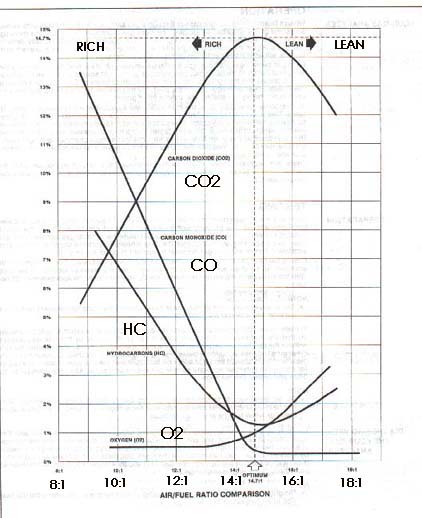 Diagram courtesy of MPSI Emission Control Training Manual You can watch the fuel injector pulse width change back and forth on an oscilloscope screen and if you connect up the O2 voltage signal on channel 2 and the fuel injector signal on channel 1 of the o-scope. You will see how the high (rich) O2 voltage will cause the fuel injector pulse width will be reduced in order to lean out the mixture. NOTE: If the Oxygen sensor or wiring fails, the ECU will use the last adaptive fuel mixture at the time of the failure [1][2] 20V ECU system information index References: [1] Audi of America, Technical service training publication: "The New 20V Turbo Engine for the Audi 200 Quattro-publication [2] "Motronic Engine Management System for the Audi S4 and the 4.2 Liter Audi V8" All rights reserved. Copyright © SJM Autotechnik™ , all rights reserved Return to Troubleshooting Tips page. Return to SJM Autotechnik™ main page. |
| About Us Privacy Policy Terms of Use Links Customer Service Safety Information Home |